system integration
Stable, secure, elastic and high-performance cloud computing services to meet your diverse business needs in real time 当前位置:系统集成
Voice data integration scheme
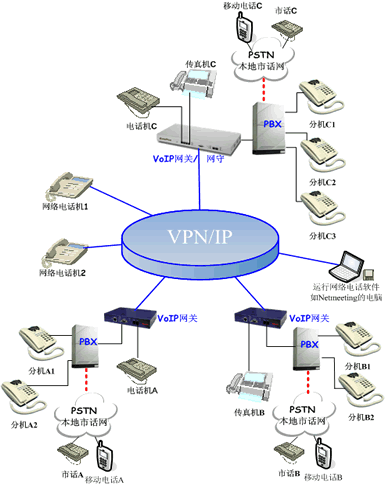
The more branches or partners an enterprise or organization has, the more necessary it is for departments to communicate with each other. If more and more customers of an enterprise feel that they are not suitable for one branch, the number will be released. Moreover, the branches of most enterprises in different regions must have different division of labor and different advantages. How to strengthen the internal humanized communication between various departments of enterprises or institutions? How to make customers feel that the enterprise is an orderly and easy to communicate organization, rather than a scattered organization that is difficult to communicate? How to make use of different backgrounds and advantages? These problems are the most concerned problems of enterprise management. Program summary: Scheme summary: the maturity of network technology provides a good foundation for solving these problems. So can sending and receiving email or simply sharing data resources through the network solve the problem? The answer is yes, absolutely not. On the one hand, not all employees in any company are proficient in it. In this era of increasingly fragmented career, staff in different departments have different majors and different business contents to learn. And some of the things transmitted in the network can never be as clear and concise as the language expression. So, can it work to rent the function of the program-controlled exchange of Telecom, or to set up a call center? Of course, it is certainly possible to rent nationwide, make use of the functions of Telecom telephone exchanges, or set up call centers across regions. However, the high rental cost is bound to increase the operating costs of enterprises, which enterprises or institutions certainly do not want to see. So is there any cheap and practical solution? So, can it work to rent the function of the program-controlled exchange of Telecom, or to set up a call center? Of course, it is certainly possible to rent nationwide, make use of the functions of Telecom telephone exchanges, or set up call centers across regions. However, the high rental cost is bound to increase the operating costs of enterprises, which enterprises or institutions certainly do not want to see. So is there any cheap and practical solution? Naturally, the answer is yes. VoIP (voice over IP) technology provides the best solution for the above problems. It uses IP technology to transmit voice with a bandwidth of less than 10k. Moreover, with the extensive application of DSP (digital signal processing) chips and the cooperation of flow control, VoIP gateway can solve many difficult problems for you, and let you care about your specialty and your field. Features of the scheme: As shown in the right figure, take gateplus voice gateway as an example: 1. It can provide free calls from branch to branch, such as free calls from extension A1 to extension B1 and extension C1. 2. Realize free call from network telephone to each extension. Such as network telephone 1 to extension A1, B1, etc. 3. Realize the free call between the computer running the network telephone software and each extension and the network telephone. 4. Use the skip dial function, combined with local telephone, to realize the communication between VoIP and local telephone. As shown in the figure, for the call from extension A1 to local telephone C or mobile telephone C, only the local telephone fee at local telephone C or local mobile telephone fee at mobile telephone C is charged. 5. Use the skip dial function, combined with local telephone, to realize the communication between VoIP and local telephone. As shown in the figure, for the call from local telephone a to local telephone C or mobile telephone C, only the local telephone fee of local telephone a and local telephone C or the local mobile telephone fee of mobile telephone C will be charged. 6. Gateplus series VoIP products also have more powerful functions such as hotline, embedded gatekeeper (some models), voice enhancement, etc |